Windows Remote Desktop: 6 ways to fix the issues. Windows Remote Desktop is an excellent tool to connect various devices over the local network. It enables you to access the resources of one device (remote/target PC) on another computer (local PC).
However, the connection between windows desktop and its host computer may fail for several reasons. Some of the common remote desktop issues include:
- Network failure
- Security certificate issues
- Unmatched login credentials
- Authentication errors
- Firewall problems
When such remote desktop failures happen, you need to perform some remote desktop troubleshooting to detect and sort out the issues.
There are several solutions that can resolve issues with windows remote desktop. In this article, we share six ways that will fix your remote desktop and get it up and running.
Table of Contents
1. Verify that Remote Desktop is enabled on the host PC:
To be able to connect a local and host PCs, you need to make sure that the remote desktop feature is enabled on the PC you want to access. Follow these steps to check the status of the remote desktop feature on the device:
- Click Start and select Settings
- Click on the System icon in Settings and look for the Remote Desktop tab
- Check the button next to the Remote Desktop tab. RD won’t work in case the button is turned off.
Turn on the button to Enable Remote Desktop and click Confirm.
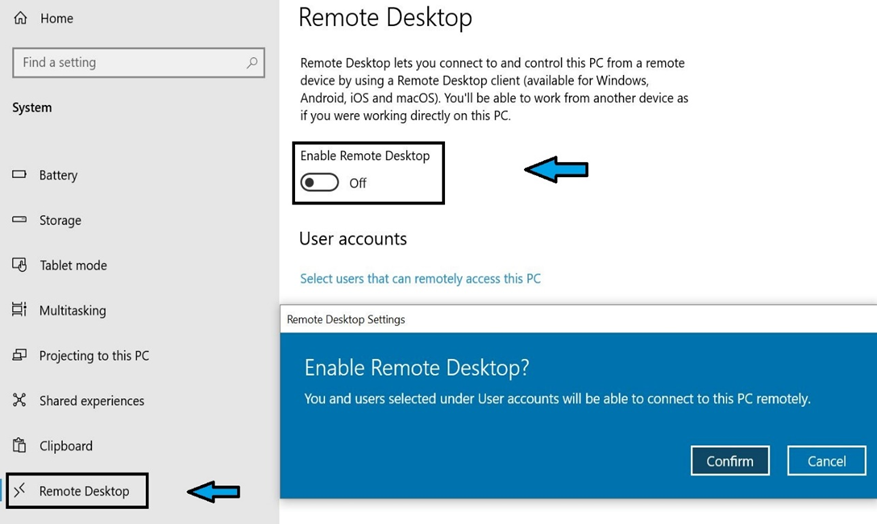
It is pertinent to note that a PC can be accessed only if it can be discovered by other devices in the network. Tick both the boxes below the RD tab to enable access.
2. Network connection:
An unstable internet connection is a common reason for RDP failures. Test your internet connection to ensure that the network resources work the way they should. You can perform a ping test to find possible network problems.
Type cmd in the Command Prompt and use the following command:
ping 8.8.8.8
In case you encounter connectivity issues, you can check your IP configuration with the command below:
ipconfig
The command will list your server network connections, including the private network, IPV4, and IPV6. If you spot a difference in your server network details and the output of ipconfig, you should ensure that all the network interfaces should automatically obtain IP addresses. You can do this by following these steps:
- Open Network Connections from the Start menu
- Click on Properties for any of the Ethernet adapters
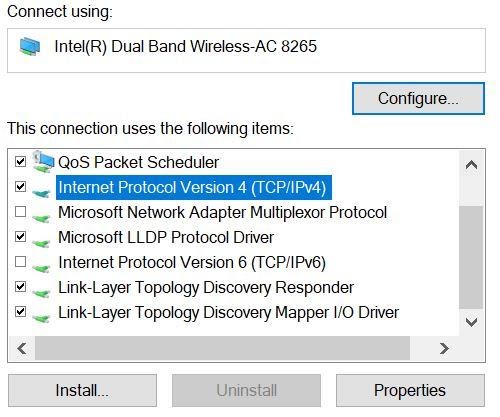
- Click IPv4 or IPv6 and select Properties
Set the radial buttons to automatic and click OK
3. Check the status of RDS:
Remote Desktop errors can arise if RDS, short for Remote Desktop Services, fails to start on either the local or the remote computer. These services include:
- TermService
- UmRdpService or Remote Desktop Services UserMode Port Redirector
If any of the services are not running, you need to start them to enable remote access. You can enable these services by typing the following command in CMD:
Net start TermService
If the TermService is already running, the command window will display a message that reads, “the requested service has already been started.”
If TermService is disabled through a registry hack, the above command won’t be able to start the services. You can fix this with a registry change command.
reg add “HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server” /v TSEnabled /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f
Reboot the system for the changes to take effect. After the system reboots, the terminal services shall automatically start. You can also use the net command to start the services manually.
4. Change Firewall settings:
The Antivirus and Windows Firewall settings can also contribute to Remote Desktop connectivity issues. To avoid firewall errors, make sure that the port your RDP software uses is open on firewalls residing on the target PC and the server they connect to.
It’s quite common to see public networks block Remote Desktop traffic. You can check firewall settings with these steps:
- Go to Control Panel by typing Control in the Run window
- Select System and Security in the Control Panel window
- Look for Windows Defender Firewall
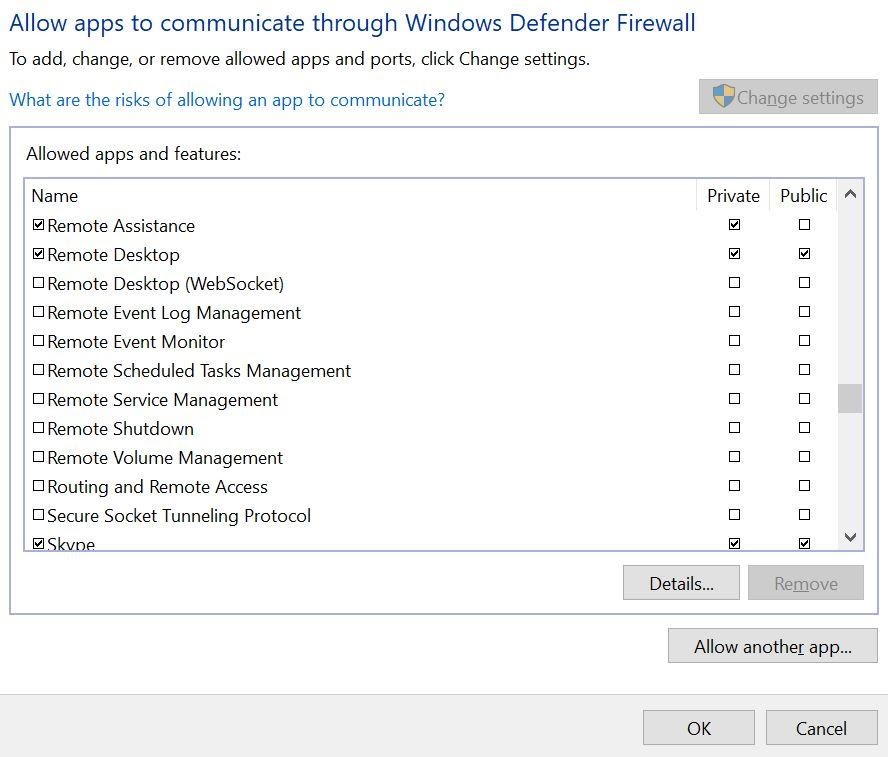
- Click on ‘Allow an app through Windows Defender Firewall’
- Find Remote Desktop and tick the box next to it
- Click OK to save changes
5. Edit or delete your Remote Desktop Credentials:
Remote Desktop issues can also arise due to unmatched Remote Desktop credentials. To fix this problem, you’ll need to edit or reset your credentials. Below is how you can resolve the issue:
- Enter Remote Desktop connection in the search box in the Start menu
- Enter the remote PC’s IP address. If the host computer already contains credentials for the remote PC, you will see the options to edit or delete them.
- Click delete to expunge the credentials
After you have removed the credentials, try to reconnect the remote computer and see if the error is fixed.
6. Disable IPv6:
Disabling IPv6 (Internet protocol) on your adapter is also known to fix ‘remote desktop not working’ errors. Windows tend to use IPv6 over IPv4 by default. If you’re having trouble using IPv6 to connect to servers, you can manually set the system to use IPv4. This is how you can do it.
- Go to Settings and find Network and Internet
- Select Ethernet followed by the Change Adapter option
- Right click on the intended adapter and select Properties
- Find TCP/IPv6 in the options and uncheck the box in front of it
- Click OK and reboot the system
This will force the computer to use Internet Protocol version 4 to connect to the servers. Now check if you can access the remote desktop.
Summing up:
The solutions in this post will hopefully help you fix connection problems with a remote desktop. If you are still unable to resolve your RDP issue, reach out to your network provider or an expert for reliable connectivity and uninterrupted workflow.












